
Closed reduction refers to setting the break without cutting the wrist open surgically. Treatment for children is usually with closed reduction and immobilization in a cast that goes up above the elbow. CT scans aren't routinely ordered but may be necessary.
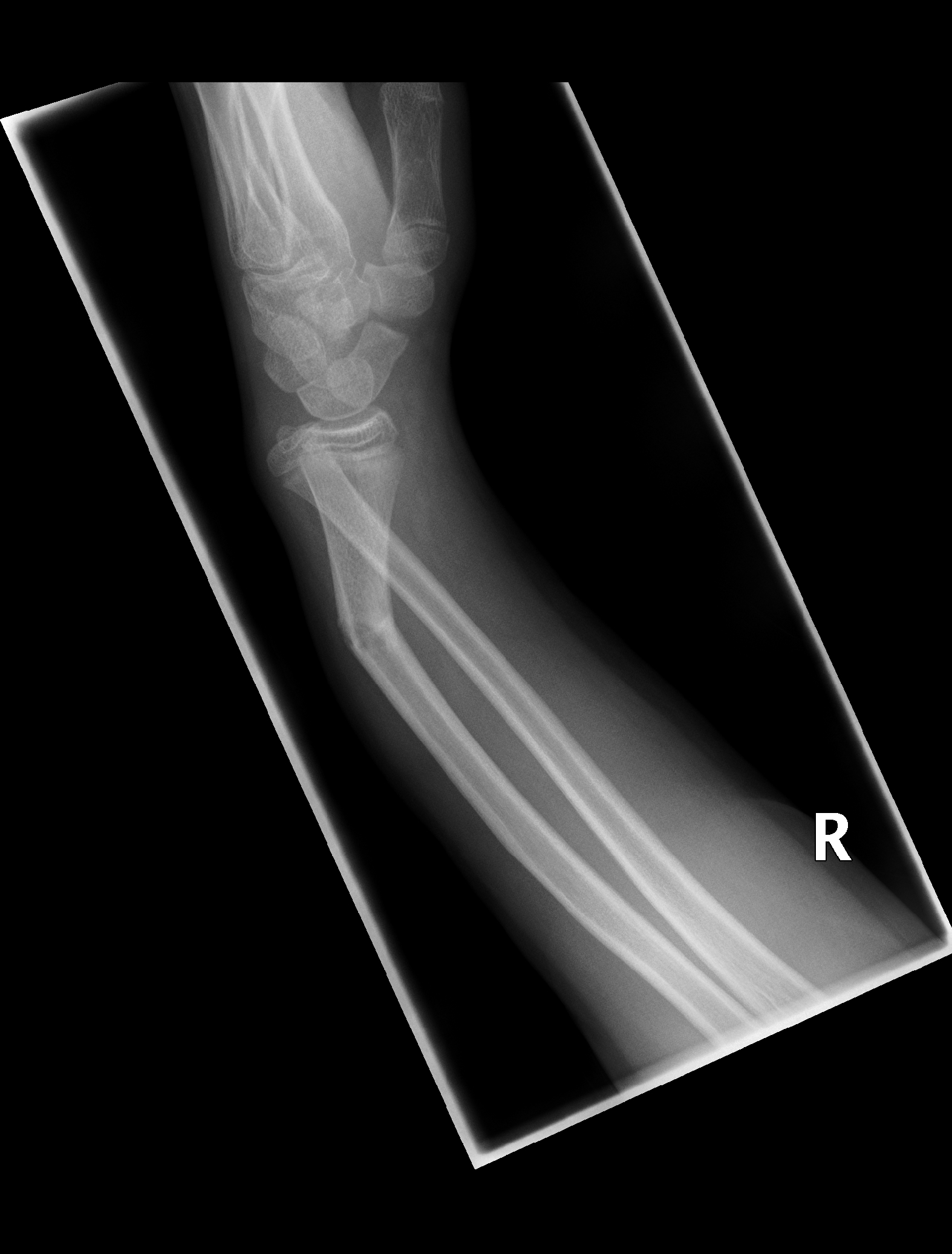
Studies show that 20 per cent of true distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) injuries won't show up on an X-ray. Some of the worst results occur because of a failure to identify (and treat) all of the soft tissue injuries.Īfter hearing the history of what happened and examining the injury, the surgeon will order X-rays.
#Galeazzi fracture full#
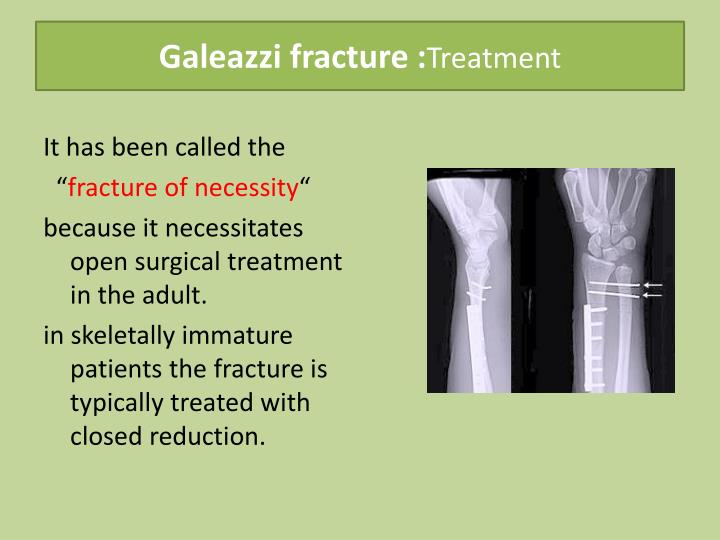
What can be done to manage this problem? First, an accurate diagnosis and discovery of the full impact of the damage is important. For children, involvement of the growth plate creates some additional potential problems. Treatment is similar but has some differences depending on age and severity of the damage done. Children and adults can both have this type of fracture. Turning door knobs, picking up groceries, even toileting can be difficult if not impossible. Muscles in the forearm add their own forces on the broken bone causing further deformities.Ĭombined together, the result of a Galeazzi fracture can be very disabling causing significant functional limitations. If that's not bad enough, without this important soft tissue structure, the fractured radial bone jams up on itself causing a shortening of the bone. The soft tissue at that junction is called the triangular fibrocartilage or TFCC. Along with dislocation of the two bones comes a rupture of the fibrous cartilage where the two bones meet the carpal (wrist) bones. Other events such as car accidents, electric shock, and blunt trauma can also result in a Galeazzi wrist fracture.ĭislocation of the radius and ulna is a key feature of the Galeazzi fracture. The force of the impact causes the break. Most of the damage is done when the person falls with an outstretched arm and lands on the wrist with the hand bent back into full extension. The interosseous membrane - ligaments that hold the two bones together along the length of the bones can be torn when the force of the injury is forceful enough. Some experts who have studied this problem say Galeazzi fractures occur when the distal one-third of the radial shaft is broken.īut it's more than just the bone because the fracture causes a disruption of the joint where the radius and ulna are connected together. The main area affected is the shaft of the radius (forearm bone) down at the end closest to the wrist. Let's start with a quick description of the fracture. If you have this type of fracture (or know someone else who does), then this article will help you understand all the complexities of this injury. From there, they cover diagnosis and treatment with a follow-up on complications and prognosis. They begin with a description of the fracture, then review the anatomy, and describe the mechanism of injury that causes these fractures. In this article, orthopedic hand surgeons present a review of Galeazzi fractures from top to bottom. A fracture that disrupts the DRUJ is called a Galeazzi fracture. That particular joint at the wrist is called the distal radioulnar joint or DRUJ. Those two bones meet at the elbow and at the wrist. This article is focused on fractures of the joint between the two bones of the forearm (the radius and the ulna). Misdiagnosis or inadequate management of Galeazzi fracture may result in disabling complications, such as DRUJ instability, malunion, limited forearm range of motion, chronic wrist pain, and osteoarthritis.There are several different types of fractures that affect the wrist. Further intraoperative interventions are based on the reducibility and postreduction stability of the DRUJ. Anatomic reduction and rigid fixation should be followed by intraoperative assessment of the DRUJ. Open reduction and internal fixation is the preferred surgical option. In adults, nonsurgical treatment typically fails because of deforming forces acting on the distal radius and DRUJ. Nonsurgical management with anatomic reduction and immobilization in a long-arm cast has been successful in children. Underdiagnosis is common because disruption of the ligamentous restraints of the DRUJ may be overlooked. Diagnosis is established on radiographic evaluation. Typically, the mechanism of injury is forceful axial loading and torsion of the forearm. Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the radial diaphysis with disruption at the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). J Am Acad Orthop Surg October 2011 Kivanc I. GEOPS (Grupo de Estudio de la Osteoporosis).



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
